Symptom: joint pain.
Possible causes: trauma, arthritis, arthrosis, arthrosis.
Doctor: The therapist records complaints, submits them for examination and, based on his results, will refer the patient to a doctor with a narrower specialization.
Treatment: prescribed individually in each case.
Prevention: reducing the load on the joints, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, timely examination by a doctor, diet.
Why do the joints hurt?
Joints can hurt for two reasons: arthritis, inflammation of the tissues of the joint or arthrosis (osteoarthritis), a degenerative-dystrophic process, that is, destruction of the cartilaginous elements of the joint. The diagnosis should be made by a doctor, but you can navigate the symptoms yourself.
Inflammation in arthritis is like a forest fire: everything starts violently, the joint swells and hurts a lot even at rest, and when you try to make the slightest movement, the pain intensifies. The skin in this area turns red and becomes warm to the touch.
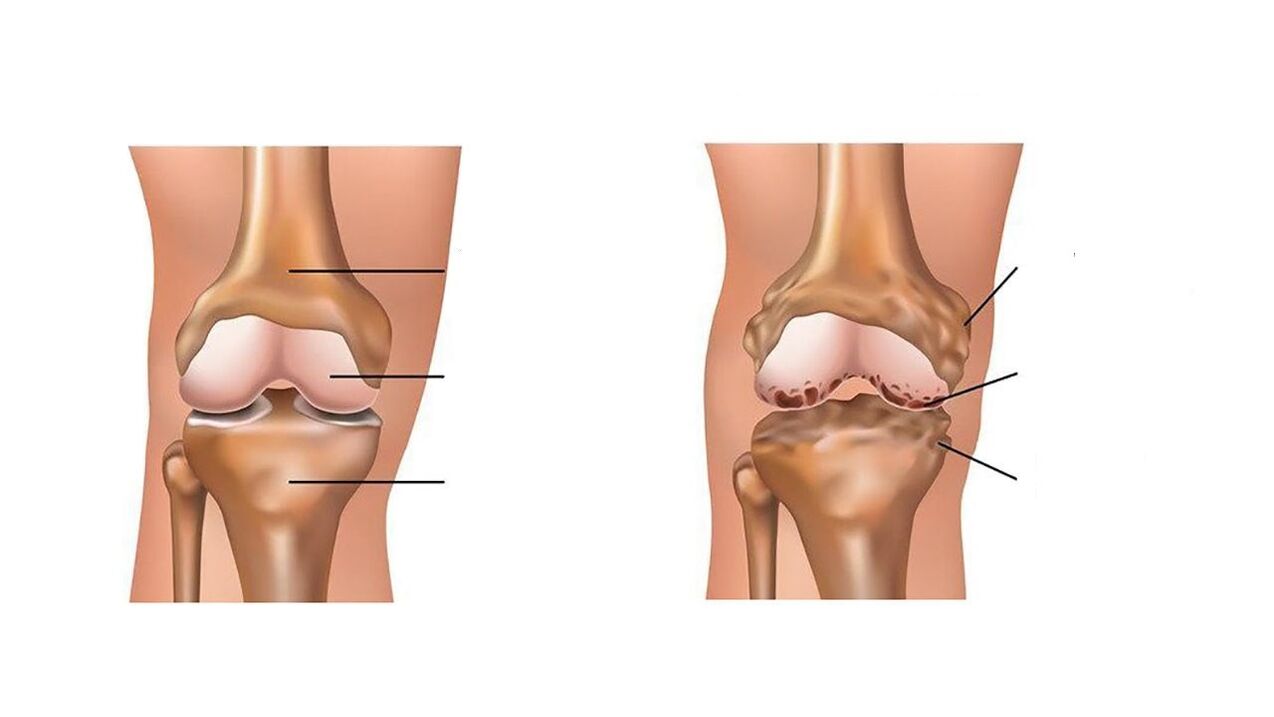
With osteoarthritis, everythingis different: the joints are initially destroyed slowly and imperceptibly. Joint pain, initially mild, aching, which occurs only during movement, quite bearable, increases over time, becoming constant and severe enough to disturb peace and sleep. The pitfall of this pain is that it is delayed in relation to the pathological process that takes place in the joint, and occurs only when the radiographic images show signs of destruction of the corresponding joint, unfortunately irreversible. This is the proliferation of spines (marginal osteophytes) along the edge of the articular surfaces of the bones that form the joint, narrowing of the joint space and signs of osteosclerosis - areas of pathological increase in bone density. If osteoarthritis affects a joint, such as the knee, the biomechanics changes and the function of the adjacent joints - the hip joint and the ankle - is disrupted. They undergo a greater load and, at the same time, uneven and, consequently, wear out faster. Therefore, osteoarthritis affects joint by joint and the pain intensifies and can spread to all new joints.
Types of pain
The type and nature of pain sensations depend on the cause that caused them.
Joints hurt with flu and acute respiratory infections against a background of high temperature (up to 40 ° C). This pain disappears on its own as soon as the temperature returns to normal and does not require special treatment.
For arthritis pain:
- acute,
- painful,
- button
- shot,
- occurs at rest and intensifies during the execution of certain movements,
- donate to neighboring areas,
- during probing (palpation) it hurts everywhere, over the entire surface of the joint, but especially along the joint space.
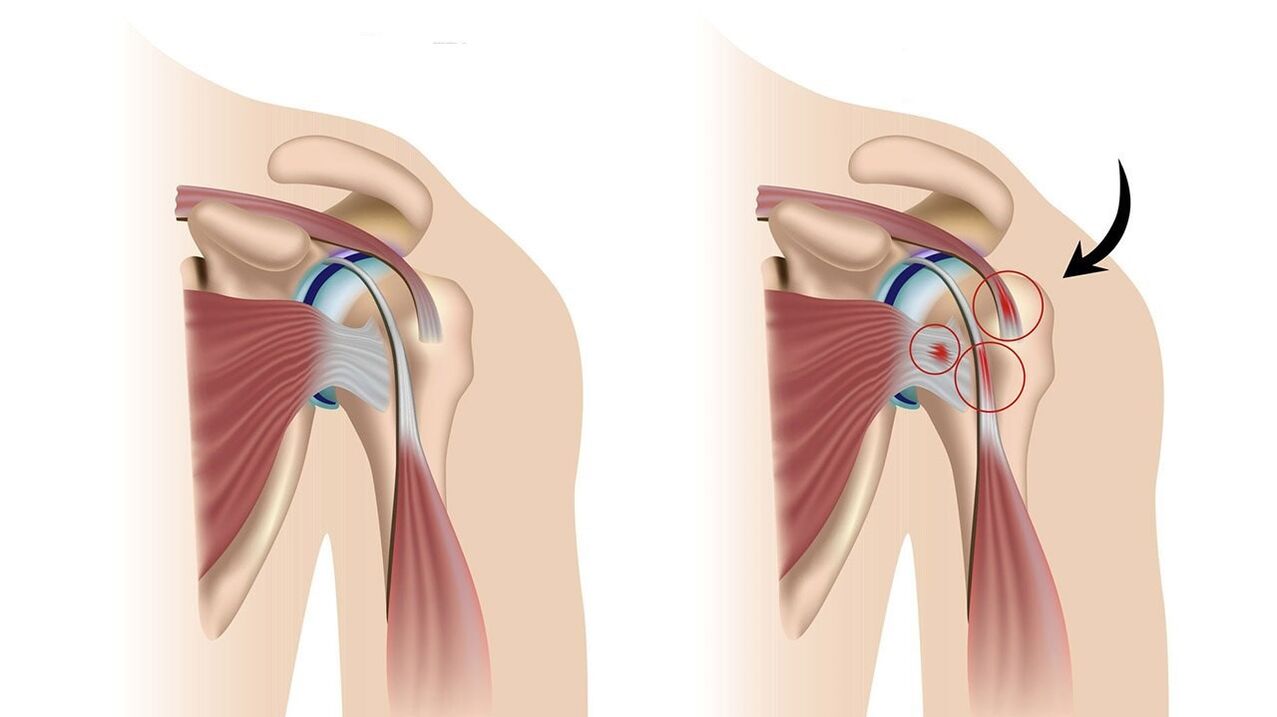
Periarthritis is particularly unbearable: inflammation of the tissues around the joint (sacs, tendons and ligaments). How it all happens can be explained by the example of the shoulder joint. First, the joint starts to hurt. The pain very quickly becomes excruciating, almost unbearable. It radiates to the shoulder blade and neck area, intensifies (and is often accompanied by a crunch) when trying to stretch the arms to the sides at shoulder height or bend them at the elbow and bring them behind the back. At the end of the collarbone, which rests on the shoulder joint in front, and in the same place in the back there are sore spots. When you press them with your finger, the pain increases. With such acute sensations, the joint needs immobilization: the hand must be hung on a handkerchief, try not to move it. This is an essential condition for the success of the treatment.
Important! as soon as possible choose adequate analgesic and anti-inflammatory therapy after the examination. This will reduce the severity of joint inflammation, reduce pain, and improve quality of life.
With osteoarthritis, joint pain is different:
- The pain is initially mild and inconsistent, its character is undulatory - in certain periods it is absent for weeks or even months. But over time, without treatment, the waves of pain become stronger and more frequent, and the spaces between them shrink.
- Pain in the beginning: its explosion occurs at the first attempt to take a step, raise an arm, bend. Then the joints appear to be developed and the pain subsides.
- Mechanical rhythm: the joint starts to ache when you load it. At first, pain appears with high loads - lifting weights, running up stairs, walking for a long time, playing sports. Later, even minor movements echo the pain. But at the same time, unlike unpleasant sensations in arthritis, pain in arthrosis disappears when you give the joint rest, you give it peace. That's why doctors talk about mechanical rhythm: movement causes pain and rest relieves it.
- Discomfort at night. There is no pain at rest as such, but lying down is uncomfortable, whenever you want to change your posture, find a position where you may forget your joints and spine, but it doesn't work. Joints hurt, that's all! The chains of the morning: wake up, there is still no pain, but it was as if you were chained or bandaged tightly - the joints do not obey, but gradually the feeling of stiffness disappears, the range of motion in the joint is restored.
- Protective posture. When a joint hurts, you want to take the so-called analgesic position, an analgesic position, in which it becomes easier. This is best seen in the example of the spine: it is also made up of joints. When one of them wedges and with it a nerve root enters the bone grip, there is a sharp pain on the basis of sciatica. Anyone can diagnose a sciatica sufferer after seeing how distorted the poor man is. In fact, with the help of this "asymmetry", supported by the muscle spasm, the body tries to minimize the pain.
Osteoarthritis of the hip and knee
Pain with a hip joint injury (and most often suffers on one side) is localized in the upper thigh and radiates to the knee. Usually he begins to get sick in the second half of the day, when he has already worked a lot. The pain increases with walking and at rest it weakens and disappears.
The knee joints most often suffer from both at the same time. They spread out easily and start to hurt when they bend over. The so-called ladder symptom is characteristic of knee injury. Getting off it becomes more painful than climbing; patients do this by turning sideways. Sometimes the joint is wedged into a bent position due to bone growth (osteophyte) or its fragment (such a "lost" bone fragment within the joint is called a "joint mouse"). Joint blockage is accompanied by increased pain when trying to bend or straighten it.
Knee mobility problems aren't always associated with arthritis. Sometimes the joint wedging can be "false". Among the most common causes of knee pseudoblock are:
- Edema (excess fluid in the joint capsule can interfere with complete flexion and extension of the joint).
- Inflammation (inflammation of the tissues of the knee, such as in rheumatoid arthritis and gout).
- Incorrect movement of the patella in the joint (accompanied by severe pain).
- Irritation of the tissue lining the joint.
- Knee injury (Any serious knee injury, such as a sprain, can cause muscle spasms).
Important! If the joint is jammed, active movements in the joint are impossible, it is necessary to seek medical assistance from an orthopedic traumatologist as soon as possible: an emergency room, a clinic, a hospital. Don't hesitate to call the ambulance - this is a good reason to call, as you won't go far on one leg and you may not even get to the clinic on your own.
Diagnostics
Due to the nature of the pain and the appearance of the affected joint, a preliminary diagnosis (arthritis or osteoarthritis) can also be made by a non-specialist. But hurry to the district clinic for confirmation of the assumptions!
Which doctor should I go to?
If you have joint pain, you should make an appointment with a local therapist. It performs the functions of a medical manager: records complaints and clinical symptoms, directs the patient for examination and, based on its results, decides which doctor should consult each particular patient. A wide variety of specialists are involved in maintaining joint health:
- arthrologist.
- orthopedic traumatologist.
- rheumatologist.
- vertebrologist (if the spinal joints are affected).
- podiatrist (when it comes to the joints of the foot).
- surgeon.
- oncologist.
- neurologist (if the joint has already been treated, but the pain remains in it).
- dietician (if the joints hurt due to metabolic disorders, such as gout, or if there is excess weight).
What exams to pass and research to do?
The examination begins with the simplest: a clinical (from a finger) and biochemical (from a vein) blood test for signs of inflammation, as well as a general urine test. In some diseases of the joints, the kidneys are involved in the pathological process. Excess uric acid in the urine can indicate gout as a cause of joint disease.
A laboratory study of the synovial fluid, which is located inside the joint, helps to detect the inflammatory process and clarify its nature. It is obtained by puncture of the joint capsule - puncture. If necessary, a histological examination of a fragment of the synovial membrane lining the joint cavity from the inside is performed.
A proven diagnostic method is x-ray of the joint in two standard views. It will help visualize joint space narrowing, bone growths, osteoporosis and osteosclerosis (areas of reduced and increased bone density.
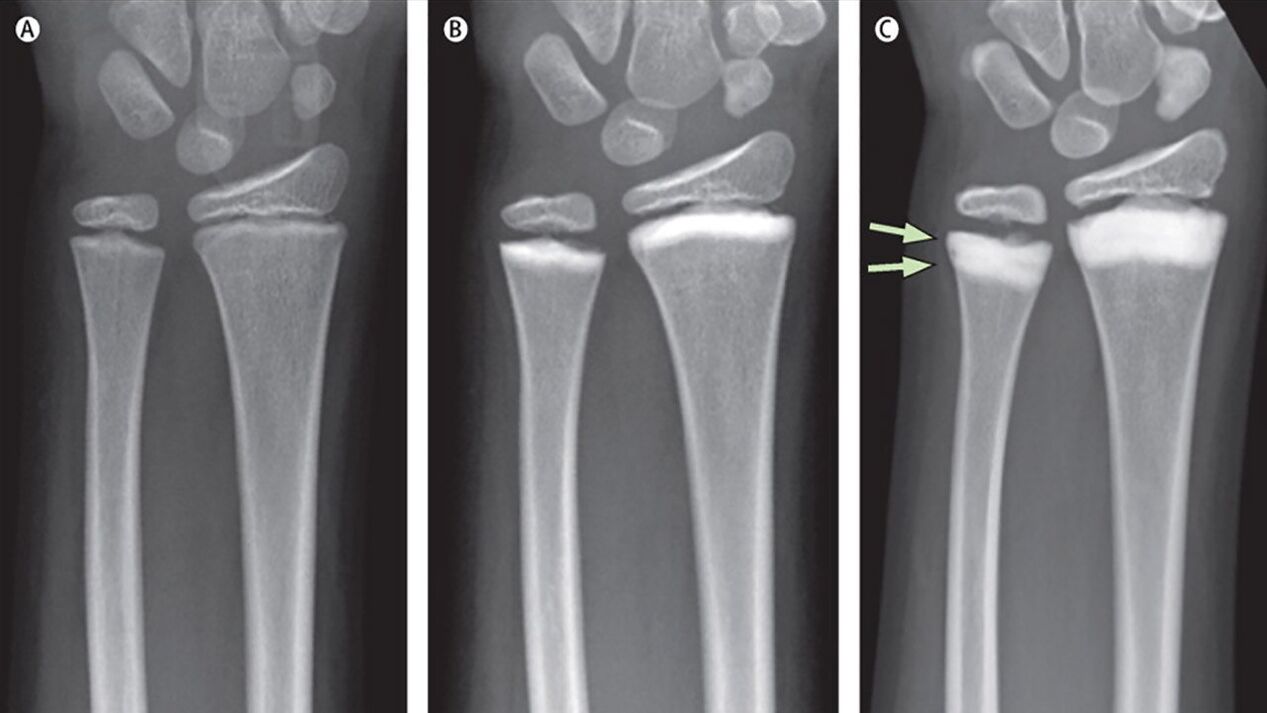
Currently, complete information on the state of the joint is provided by MRI.
What joint diseases can cause pain?
There are over a hundred of these diseases. Arthrosis is common in the elderly and rheumatoid arthritis and injuries (bruises, fractures, ligament injuries) in young people.
"Along with high blood pressure, commonly called hypertension, joint disease is at the top of the list of the most common reasons to seek medical help. And the chronic pain that patients experience at the same time and due to which they cannot live and work fully does notit is only a medical problem, but also an important social problem, - says the doctor of medical sciences, professor of the rheumatology department. - Of all joint diseases, osteoarthritis is the most common. 97% of those over 65 suffer fromthis disease. And if we talk about chronic inflammatory diseases of the joints - arthritis, here rheumatoid arthritis comes to the fore. It is not even a gift, and not only for pain syndrome: within 3-5 years of its onset, this typeof arthritis inevitably ends with the assignment to the patient of a disability group ".
How to get rid of joint pain urgently?
Analgesics are able to overcome pain quickly: pain cannot be tolerated in every case, if you do not want it to turn from acute to chronic. This metamorphosis can happen very quickly - in 3-4 weeks, so getting rid of joint pain should be an urgent task. The joint starts to hurt as soon as you put stress on it. Therefore, in case of pain, a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) with a good analgesic effect should be taken half an hour before any physical activity.
If joint pain worsens during the night, in addition, before going to bed, the doctor will recommend taking metamizole sodium and drotaverine with nicotinic acid to improve local blood circulation.
Local therapy
NSAIDs have a formidable side effect: they can cause damage to the gastric mucosa up to the formation of ulcers, so try to apply them locally, as part of all kinds of ointments and gels with anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties. They are usually rubbed into the skin over the affected joint twice a day. The pain is also relieved by special magnetic powder patches, which are glued to the joint or spine.
What happens if the joints are not treated?
Joint disease, if left untreated, can lead to loss of freedom of movement and disability. If one or more large joints are affected, they can be replaced with artificial ones. Multiple joint damage (polyarthritis), as a rule, is a consequence of a general disease of the body, for example, psoriasis. In this case, it is all the more dangerous to start the disease, because it progresses rapidly and can end your life rather quickly.
Conclusion
Joint pain is familiar to almost everyone and occurs for two main reasons: due to inflammation (arthritis) or the destruction of bones and cartilage (osteoarthritis). Interestingly, the joints in the arms and legs hurt in different ways. On the upper limbs, unlike the lower ones, usually the joints themselves are not affected, but the surrounding tissues (tendons, ligaments, bags). This is due to the different type of load that the arms and legs undergo, respectively dynamic and static. Joint pain must be fought from day one: the prospect of disability in the next 10-15 years will please very few people. As part of the prevention of joint diseases, it is important to lose extra pounds to reduce stress on the joints and to cope with concomitant diseases (allergies, diabetes mellitus).
































